30 Critical Group Policy Settings to Secure & Optimize Windows
Last Updated:
Constant auto-updates, web results in search, and data collection are just a few of the many pain points for Windows users.
Windows makes it seem like these can’t be changed, but that’s actually quite easy to do using the Group Policy Editor.
This tool provides access to over 4000 policies that determine how Windows behaves and what users can/cannot do on the system.
I’ve handpicked 30 group policy settings that will net you most of the benefits regarding Windows customization, organizational security, and productivity.
Note: These policies were tested on Windows 11 version 22H2. Their location and efficacy may differ on other Windows versions.
Disable Web Results In Search
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Search\Don’t search the web or display web results in search
Enabled
Enable this policy to stop getting Bing results in Windows Search.
Disable Diagnostic Data Collection
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Data Collection and Preview Builds\Allow Diagnostic Data
Enabled > Diagnostic Data off
Configure Windows to send no diagnostic data at all.
Disable Telemetry
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Application Compatibility\Turn off Application Telemetry
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Application Compatibility\Turn off Inventory Collector
Enabled
Windows collects data on how apps use certain system components. It also collects data on your installed apps, drivers, and devices. Enable these policies to stop such tracking.
Turn off OneDrive
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\OneDrive\Prevent the usage of OneDrive for file storage
Enabled
Enable this policy if you don’t use OneDrive and would prefer to disable it on your system.
Disable Cortana in Windows 10
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Search\Allow Cortana
Disabled
Disable this policy to disable Cortana on Windows 10.
Disable Auto Updates
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Update\Manage end user experience\Configure Automatic Updates
Enabled > 2 – Notify for download and auto-install
Option 2 sets manual updates as the default update behavior on your system.
Turn Off Forced Update Restarts
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Update\Legacy Policies\No auto-restart with logged-on users for automatic updates installations
Enabled
Enable this policy to ensure that while a user is logged on, the PC won’t restart, even if an update install is scheduled.
Configure Delivery Optimization
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Delivery Optimization\Download Mode
Enabled > Simple (99)
Use the Simple download mode for Delivery Optimization (HTTP only, no peering).
The rest of the group policies are intended for organizational environments rather than personal systems.
Prevent Users From Installing Apps
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Installer\Turn off Windows Installer
Enabled
Enable this policy to stop unauthorized users from installing programs.
Disable All Microsoft Store Apps
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Store\Disable all apps from Microsoft Store
Enabled
Enable this policy to block all apps from the Microsoft Store.
Allow Launching Authorized Apps Only
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Run only specified Windows apps
Enabled
If you want to allow users to launch a few apps only, add their executable names here (e.g., Winword.exe).
Disable Launching Specific Apps
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Don’t run specified Windows apps
Enabled
If you want to prevent users from launching certain apps, add their executable names here.
Note: This and the previous policy apply to File Explorer operations (GUI) only. The blocked apps can still be launched from the CLI. To prevent this, disable CMD with the next policy.
Prevent Access to CMD
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Prevent access to the command prompt
Enabled
Enable this policy to prevent the user from running the Command Prompt and batch files.
Prevent Access to Registry Editor
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Prevent access to the registry editing tools
Enabled
The Registry Editor provides an alternative way to change all of the Group Policy Settings listed here and more. It’s crucial to enable this policy so that users can’t tweak the registry.
Hide Certain Settings From Control Panel
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Control Panel\Hide specified Control Panel items
Enabled
Disallow Control Panel items by adding their canonical names. E.g.,
- To prevent users from uninstalling programs, add
Microsoft.ProgramsAndFeatures. - To prevent access to user account settings, add
Microsoft.UserAccounts. - To prevent access to Defender or Firewall settings, add
Microsoft.WindowsDefenderandMicrosoft.WindowsFirewall.
Prevent Access to the Control Panel & Settings App
User Configuration\Administrative Templates\Control Panel\Prohibit access to Control Panel and PC settings
Enabled
Enable this policy to prevent users from opening the Settings app or Control Panel.
Block Removable Storage Drives
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Removable Storage Access\All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access
Enabled
Enable this policy to block removable drives (USB sticks, portable SSDs, etc).
Track User Login History
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Advanced Audit Policy Configuration\System Audit Policies\Logon Logoff\Audit Logon and Logoff
Enable the Configure > Success checkboxes.
You can now access the login history from the Security Logs in the Event Viewer.
Increase Minimum Password Length
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Account Policies\Password Policy\Minimum password age
Set how many characters passwords must use at minimum.
Enforce Max Password Age
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Account Policies\Password Policy\Maximum password age
Set the number of days after which the password will expire and a new one must be set.
Allow Complex Passwords Only
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Account Policies\Password Policy\Password must meet complexity requirements
Enabled
Enable this policy to enforce complex password requirements like uppercase, lowercase, numbers, non-alphabetic characters, etc.
Ensure LM Hash Storage is Disabled
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network security: Do not store LAN Manager hash value on next password change
Enabled
If the LAN Manager (LM) hash value for user passwords is stored on their PC’s security database, they can be easily compromised. Ensure this policy is enabled to prevent this from happening.
Disable LM and NTLM v1
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network security: LAN Manager authentication level
Set to Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM & NTLM.
This is the most secure challenge/response authentication protocol for network logons.
Rename Super Admin Account
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Accounts: Rename administrator account
Set a new name to make it more difficult for unauthorized users to access this account.
Ensure Anon SID/Name Translation Is Disabled
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network access: Allow anonymous SID/Name translation
Disabled
Ensure this policy is disabled to prevent anonymous users from requesting the SID of other users. This can be misused to identify account names including the administrator account.
Ensure Anon Doesn’t Have Everyone Access
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Network access: Let Everyone permissions apply to anonymous users
Disabled
Anonymous connections to a PC should be given limited well-defined permissions. Adding them to the Everyone group is not a good idea. Ensure this policy is disabled to remove the Everyone SID from the anonymous token.
Ensure Super Admin Account Is Disabled
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Accounts: Administrator account status
Disabled
Disable this policy to set the status of the hidden admin account to disabled.
Ensure Guest Account Is Disabled
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\Accounts:Guest account status
Disabled
Disable this policy to ensure the guest account is disabled.
Ensure UAC is Enabled
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\User Account Control: Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode
Enabled
Enable this policy to ensure User Account Control (UAC) is functional.
Disable WiFi Sense
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Network\WLAN Service\WLAN Settings\Allow Windows to automatically connect to suggested open hotspots, to networks shared by contacts, and to hotspots offering paid services
Disabled
WiFi Sense was designed for convenience, but it is a security risk. Disable this policy to ensure users can’t access this feature.
Customize and Secure Your PC
Group Policies are a good place to start, but remember, you don’t have to stop there.
If you’re customizing your own PC, there are plenty of themes to try, and apps / extensions to install.
Or if you’re managing a large number of PCs, consider educating your users on internet safety habits, password best practices, and malware signs.
How to Change Group Policy Settings
On individual PCs, use these steps for reference:
- Press Win + R and enter
gpedit.mscto open the Local Group Policy Editor. - Locate the policy that you want to configure. E.g.,
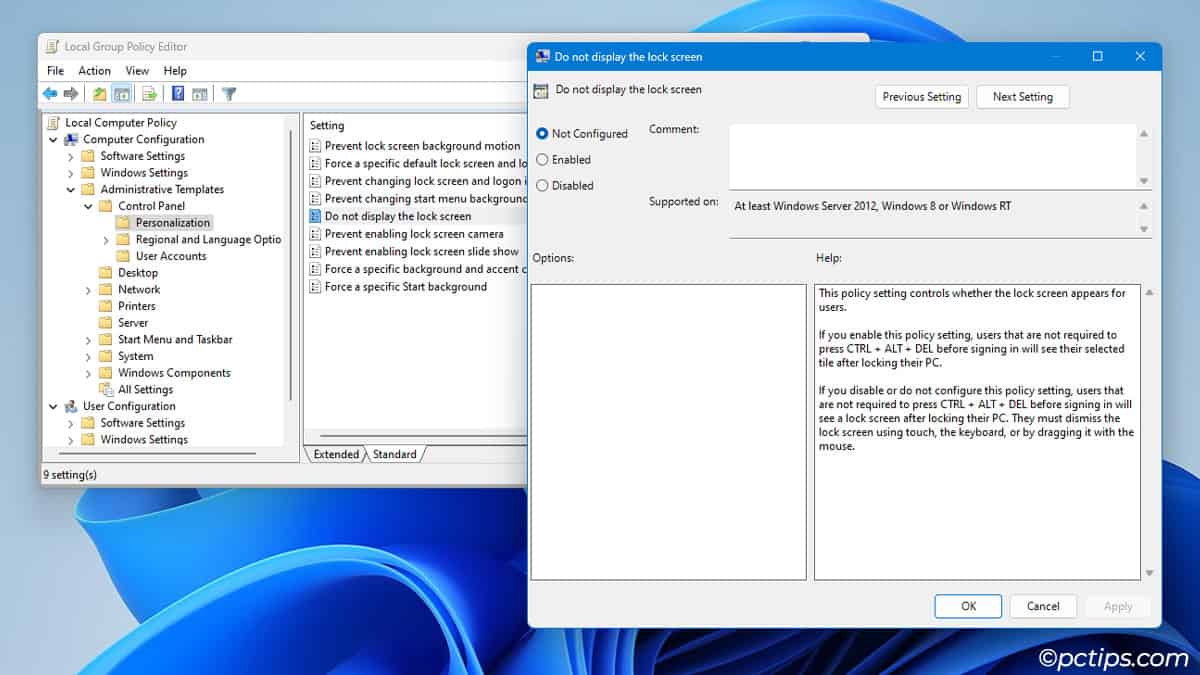
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Control Panel\Personalization\Do not display the lock screen
- Double-click it and read the help description.
- Choose to Enable or Disable the policy, then press Ok.
For AD environments,
- Access the Server Manager dashboard and select Tools > Group Policy Management.
- Expand your domain, right-click Default Domain Policy, and select Edit.
- Now, follow the same process as above to locate and configure policies.
Why Should You Change Group Policy Settings
Group Policy is a platform for managing and configuring Windows settings and user permissions from one central location.
From restricting unauthorized remote access to creating custom password requirements, it lets you manage various aspects of Windows.
It’s a useful tool for any user. Being able to change the parts of Windows that you don’t like is always convenient.
But where this tool really shines is in a domain environment. After all, it was designed to help manage groups of computers.
- When a lot of computers and users are involved, the security risk rises exponentially. Configuring security policies correctly is essential to minimize attack vectors and prevent breaches.
- Ensuring a smooth user experience is essential for productivity. Instead of asking every user to configure Windows settings, mapped network locations, shortcuts, and so on, configuring the Group Policy once is way more efficient.
- For network admins, Group Policy is an invaluable tool. Having the same set of configs across an organization makes management and future deployments much easier.